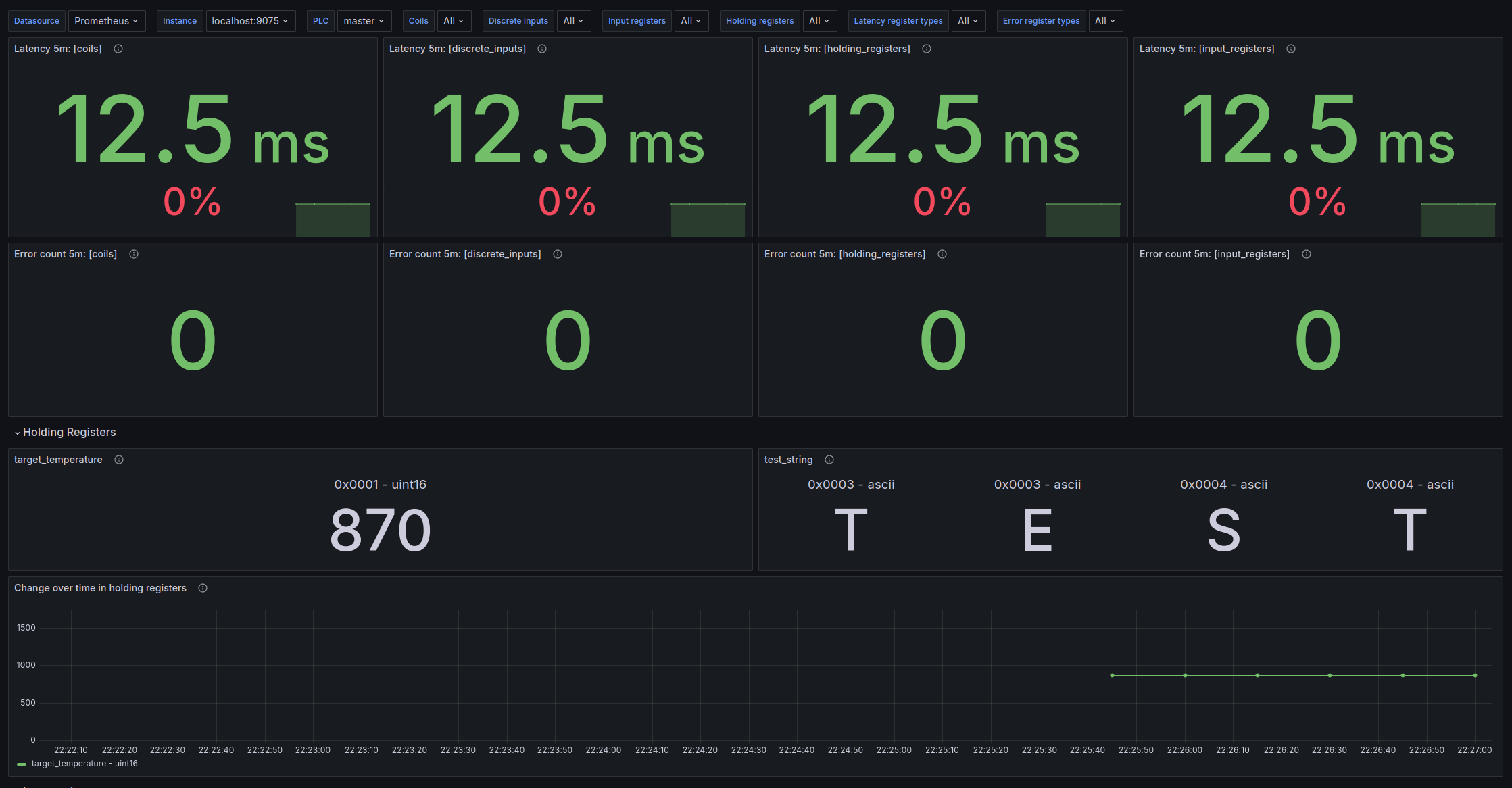
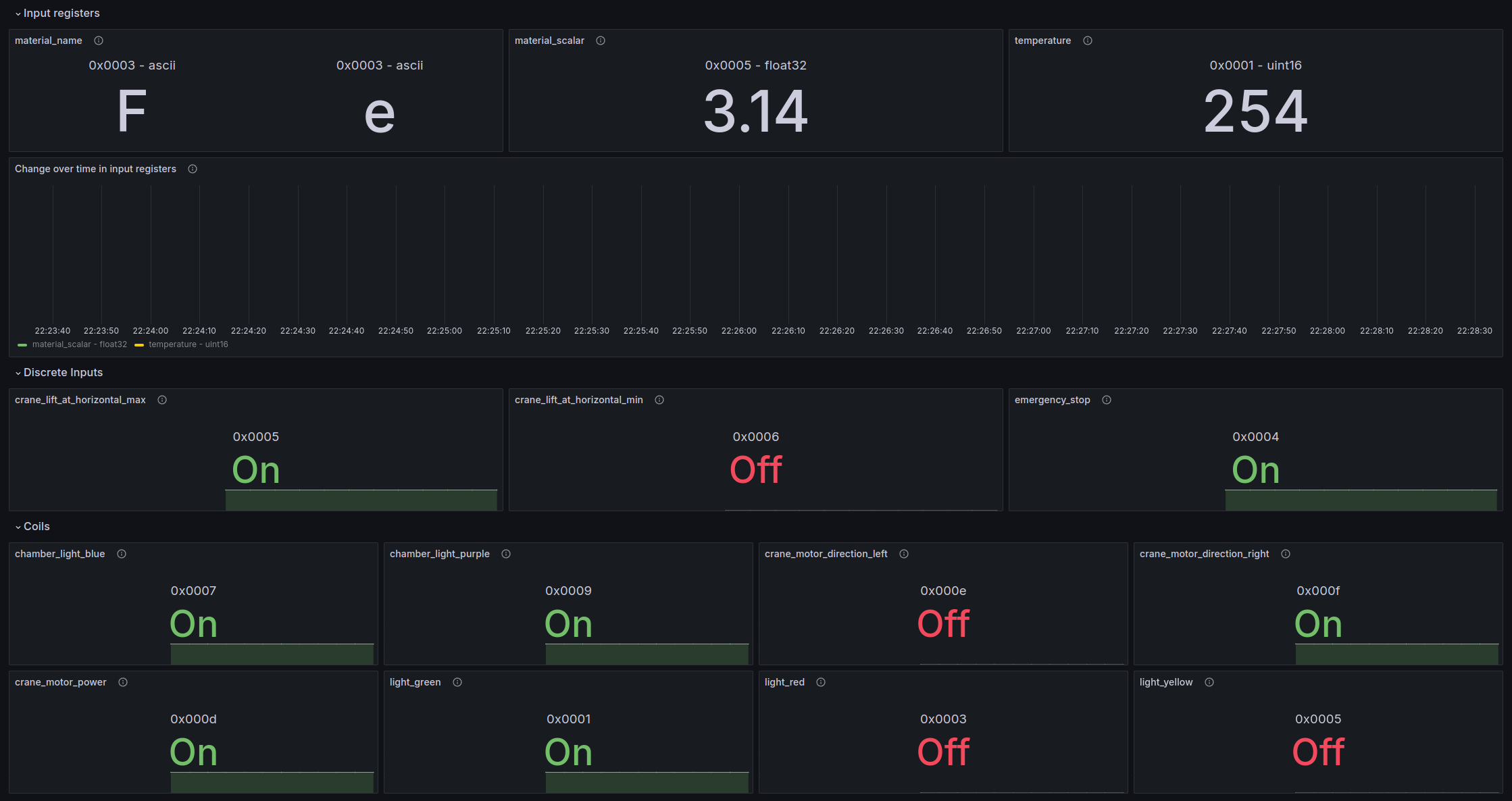
This is a simple metric exporter and dashboard provider for PLCs. It uses pymodbus to read variables from the PLC given a configuration file and exposes them as Prometheus metrics.
Install the exporter using pip:
pip install plc_exporterRun the exporter using the following command:
plc_exporter --config /path/to/config.yamlThe exporter is also available as a docker image:
docker pull ghcr.io/sourcehawk/plc-exporter:latestTo run the docker image, use the following command:
docker run \
--name myplc \
-p 9075:9075 \
-v ./examples/config.yaml:/config.yml \
ghcr.io/sourcehawk/plc-exporter:latest \
--config=/config.ymlThe exporter is configured using a YAML file. See the base config for the structure.
| Parameter | Description | Allowed Values |
|---|---|---|
| name | Descriptive name for the coil | Letters, numbers and underscores |
| description | Explanation of what the coil does | Any string |
| address | Address of the coil in hexadecimal or decimal format | hex 0x0000 to 0xFFFF or int 0 to 255 |
| type | Data type of the input register value | bool |
| Parameter | Description | Allowed Values |
|---|---|---|
| name | Descriptive name for the discrete input | Letters, numbers and underscores |
| description | Explanation of the input's function | Any string |
| address | Address of the input in hexadecimal or decimal format | hex 0x0000 to 0xFFFF or int 0 to 255 |
| type | Data type of the input register value | bool |
| Parameter | Description | Allowed Values |
|---|---|---|
| name | Descriptive name for the input register | Letters, numbers and underscores |
| description | Explanation of the register's function | Any string |
| address | Address of the register in hexadecimal or decimal format | hex 0x0000 to 0xFFFF or int 0 to 255 |
| type | Data type of the input register value (default uint16) |
See types table |
| size | Number of bytes (chars) used (default 1) | 1 to 255 |
When type is set to string, the size parameter is used to specify the number of characters in the string.
| Parameter | Description | Allowed Values |
|---|---|---|
| name | Descriptive name for the holding register | Letters, numbers and underscores |
| description | Explanation of the register's function | Any string |
| address | Address of the register in hexadecimal or decimal format | hex 0x0000 to 0xFFFF or int 0 to 255 |
| type | Data type of the holding register value (default uint16) |
See types table |
| size | Number of bytes (chars) used (default 2) | 1 to 255 |
When type is set to string, the size parameter is used to specify the number of characters in the string.
| Type | Description | Size (bytes) | Register count |
|---|---|---|---|
| bool | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
| uint8 | Unsigned 8-bit int | 1 | 1 |
| int8 | Signed 8-bit int | 1 | 1 |
| uint16 | Unsigned 16-bit int | 2 | 1 |
| int16 | Signed 16-bit int | 2 | 1 |
| uint32 | Unsigned 32-bit int | 4 | 2 |
| int32 | Signed 32-bit int | 4 | 2 |
| uint64 | Unsigned 64-bit int | 8 | 4 |
| int64 | Signed 64-bit int | 8 | 4 |
| float16 | IEEE 754 16-bit float | 2 | 1 |
| float32 | IEEE 754 32-bit float | 4 | 2 |
| float64 | IEEE 754 64-bit float | 8 | 4 |
| char | ASCII character | 1 | 1 |
| string | ASCII string | User specified | Math.ceil(size / 2) |
The exporter can be configured in static or dynamic mode. In static mode, the metrics are named according to the name parameter in the configuration file. In dynamic mode, the metrics are named according to the register type and uniquely identified by the name label.
Which mode to use depends on the use case. If you are creating a dashboard that will be used for multiple devices, the dynamic mode is recommended. If you are creating a dashboard for a specific device, the static mode might be more convenient.
All metrics generated by the exporter are prefixed with the namespace parameter of the exporter configuration.
In static mode the metrics generated for all types except strings will be {namespace}_{name}. I.e if the namespace is plc and the name is inner_temperature, the metric will be plc_inner_temperature.
If the metric is a string, there will be multiple metrics with the same name but with a unique index label. The index is the position of the character in the string that is being built. Each of the generated metrics will have the value of the ASCII code of the character it represents. For example, if the name is material and the string is TEST, the metrics will be :
plc_material{index="0", value_type="ascii"}with the value84(The ASCII code forT)plc_material{index="1", value_type="ascii"}with the value69(The ASCII code forE)plc_material{index="2", value_type="ascii"}with the value83(The ASCII code forS)plc_material{index="3", value_type="ascii"}with the value84(The ASCII code forT)
In dynamic mode the metrics generated for all types will be {namespace}_{register_type}. I.e if the namespace is plc and the register type is coils, the metric will be plc_coils. If the metric was for inner_temperature of type coils and the namespace is plc, the metric will be plc_coils{name="inner_temperature"}.
All metrics have the following labels
plc: Is set to theidentifierparameter in the configuration file.start_address: The start address of the register in the PLC as a hexadecimal stringvalue_type: The type of the value (See Types table). Note that strings and characters will have the type set toascii.index: The order (index) of the character in the string (0, 1, 2, ...). If not a string, this label is set toNone.register_type(Always present instaticmetric layout. Available indynamicmetric layout forread_time_ms+error_countmetrics): The type of register (coil,discrete_input,input_register,holding_register)name(Indynamicmetric layout): The name of the metric as specified in the configuration file.
Generated from examples/config.yml with metric_layout set to dynamic.
NOTE: Removed the read_time_ms and error_count metrics for brevity.
# HELP plc_connection_up Connection status to the PLC
# TYPE plc_connection_up gauge
plc_connection_up{manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master"} 1.0
# HELP plc_coils Coils represent discrete outputs, which are binary values and are used to control physical devices like relays, motors, lights, or any output devices connected to the PLC.They can be read and written to.
# TYPE plc_coils gauge
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="light_green",plc="master",start_address="0x0001",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="light_red",plc="master",start_address="0x0003",value_type="bool"} 0.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="light_yellow",plc="master",start_address="0x0005",value_type="bool"} 0.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="chamber_light_blue",plc="master",start_address="0x0007",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="chamber_light_purple",plc="master",start_address="0x0009",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="crane_motor_power",plc="master",start_address="0x000d",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="crane_motor_direction_left",plc="master",start_address="0x000e",value_type="bool"} 0.0
plc_coils{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="crane_motor_direction_right",plc="master",start_address="0x000f",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_discrete_inputs Discrete inputs are binary values that represent the state of physical devices like sensors, switches, or any input devices connected to the PLC. They are read-only and cannot be written to.
# TYPE plc_discrete_inputs gauge
plc_discrete_inputs{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="emergency_stop",plc="master",start_address="0x0004",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_discrete_inputs{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="crane_lift_at_horizontal_max",plc="master",start_address="0x0005",value_type="bool"} 1.0
plc_discrete_inputs{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="crane_lift_at_horizontal_min",plc="master",start_address="0x0006",value_type="bool"} 0.0
# HELP plc_input_registers Input registers are 16-bit registers that store numeric values. They are read-only and cannot be written to.
# TYPE plc_input_registers gauge
plc_input_registers{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="temperature",plc="master",start_address="0x0001",value_type="uint16"} 254.0
plc_input_registers{index="0",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="material_name",plc="master",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 70.0
plc_input_registers{index="1",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="material_name",plc="master",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 101.0
plc_input_registers{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="material_scalar",plc="master",start_address="0x0005",value_type="float32"} 3.14
# HELP plc_holding_registers Holding registers are 16-bit registers that store numeric values. They can be read and written to.
# TYPE plc_holding_registers gauge
plc_holding_registers{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="target_temperature",plc="master",start_address="0x0001",value_type="uint16"} 870.0
plc_holding_registers{index="0",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="test_string",plc="master",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 84.0
plc_holding_registers{index="1",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="test_string",plc="master",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 69.0
plc_holding_registers{index="2",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="test_string",plc="master",start_address="0x0004",value_type="ascii"} 83.0
plc_holding_registers{index="3",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",name="test_string",plc="master",start_address="0x0004",value_type="ascii"} 84.0Generated from examples/config.yml with metric_layout set to static.
NOTE: Removed the read_time_ms and error_count metrics for brevity.
# HELP plc_connection_up Connection status to the PLC
# TYPE plc_connection_up gauge
plc_connection_up{manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master"} 1.0
# HELP plc_light_green Turns on the green light when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_light_green gauge
plc_light_green{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x0001",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_light_red Turns on the red light when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_light_red gauge
plc_light_red{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x0003",value_type="bool"} 0.0
# HELP plc_light_yellow Turns on the yellow light when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_light_yellow gauge
plc_light_yellow{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x0005",value_type="bool"} 0.0
# HELP plc_chamber_light_blue Turns on the blue chamber light when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_chamber_light_blue gauge
plc_chamber_light_blue{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x0007",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_chamber_light_purple Turns on the purple chamber light when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_chamber_light_purple gauge
plc_chamber_light_purple{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x0009",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_crane_motor_power Starts the crane motor when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_crane_motor_power gauge
plc_crane_motor_power{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x000d",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_crane_motor_direction_left Sets the crane motor direction to left when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_crane_motor_direction_left gauge
plc_crane_motor_direction_left{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x000e",value_type="bool"} 0.0
# HELP plc_crane_motor_direction_right Sets the crane motor direction to right when enabled (1)
# TYPE plc_crane_motor_direction_right gauge
plc_crane_motor_direction_right{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="coils",start_address="0x000f",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_emergency_stop Indicates if the emergency stop button is active
# TYPE plc_emergency_stop gauge
plc_emergency_stop{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="discrete_inputs",start_address="0x0004",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_max Indicates if the crane is at the horizontal maximum position (right)
# TYPE plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_max gauge
plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_max{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="discrete_inputs",start_address="0x0005",value_type="bool"} 1.0
# HELP plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_min Indicates if the crane is at the horizontal minimum position (left)
# TYPE plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_min gauge
plc_crane_lift_at_horizontal_min{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="discrete_inputs",start_address="0x0006",value_type="bool"} 0.0
# HELP plc_temperature The temperature reported by the sensor
# TYPE plc_temperature gauge
plc_temperature{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="input_registers",start_address="0x0001",value_type="uint16"} 254.0
# HELP plc_material_name Testing string
# TYPE plc_material_name gauge
plc_material_name{index="0",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="input_registers",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 70.0
plc_material_name{index="1",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="input_registers",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 101.0
# HELP plc_material_scalar Testing float
# TYPE plc_material_scalar gauge
plc_material_scalar{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="input_registers",start_address="0x0005",value_type="float32"} 3.14
# HELP plc_target_temperature The target temperature to set the heating element to
# TYPE plc_target_temperature gauge
plc_target_temperature{index="None",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="holding_registers",start_address="0x0001",value_type="uint16"} 870.0
# HELP plc_test_string Testing string
# TYPE plc_test_string gauge
plc_test_string{index="0",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="holding_registers",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 84.0
plc_test_string{index="1",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="holding_registers",start_address="0x0003",value_type="ascii"} 69.0
plc_test_string{index="2",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="holding_registers",start_address="0x0004",value_type="ascii"} 83.0
plc_test_string{index="3",manufacturer="test",model="test-2000",plc="master",register_type="holding_registers",start_address="0x0004",value_type="ascii"} 84.0The exporter comes with a default dashboard which requires the following configuration:
- metric_layout:
dynamic - namespace:
plc
The dashboard source can be found here. You can copy the JSON file and import it into Grafana instance.
-
(Optional) Set up virtual environment
python3 -m venv venv source venv/bin/activate -
Install the exporter
pip install -e . -
Run the exporter
plc_exporter --config /path/to/config.yaml
A generic PCL Grafana dashboard is included in the dev/grafana directory.
To develop the dashboard, or to develop a new dashboard for a specific PLC configuration, you can use the docker-compose setup.
docker compose up --buildNote that to change the exporter configuration used, you can place your new configuration in the examples directory and change the command in the plc_exporter service in the docker-compose.yml file.
plc_exporter:
hostname: plc-exporter
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile
container_name: exporter
network_mode: host
# ports:
# - "9075:9075"
volumes:
- ./examples:/configs
command:
- --config=/configs/your-custom-config.yaml # <-- CHANGED THIS LINE- Grafana will be available at http://localhost:3000 with the default credentials
admin:admin. - Prometheus will be available at http://localhost:9090.
- Alertmanager will be available at http://localhost:9093.
Note that while developing dashboards it is a good idea to save it regularly to a JSON file in the dashboard definitions directory. This way the dashboard wont get lost and can be version controlled and shared with others.
To access a PLC for development, you can use SSH tunneling to forward the PLC port to your local machine. This is done by adding a LocalForward line to your SSH config file (usually located at ~/.ssh/config).
For example, if you want to access a PLC with IP 10.0.0.10 on port 502, on a device you can add the following line to your SSH config file:
LocalForward 1502 10.0.0.10:502Then you can develop your metrics by connecting to the PLC on port 1502 from your local machine (localhost).
Host some-remote-host
Hostname 168.0.0.10
User ubuntu
LocalForward 1502 10.0.0.10:502